Mutual Fund
“Invest smart, grow together — understand mutual funds and make your money work for you.”
* By providing my details, I consent to receive assistance from Investment regarding services .
What Are Mutual Funds?
A mutual fund is a simple and smart way to invest your money. It works by collecting funds from many investors and investing that pool of money in different financial assets such as stocks, bonds, and government securities. These investments are managed by professional fund managers who aim to generate returns for all investors.
How Mutual Funds Work
You invest a certain amount of money in a mutual fund.
Your money is combined with investments from other people.
A qualified fund manager uses this combined amount to buy a diversified mix of assets.
Any profit or loss from these investments is shared among all investors in proportion to the amount they have invested.
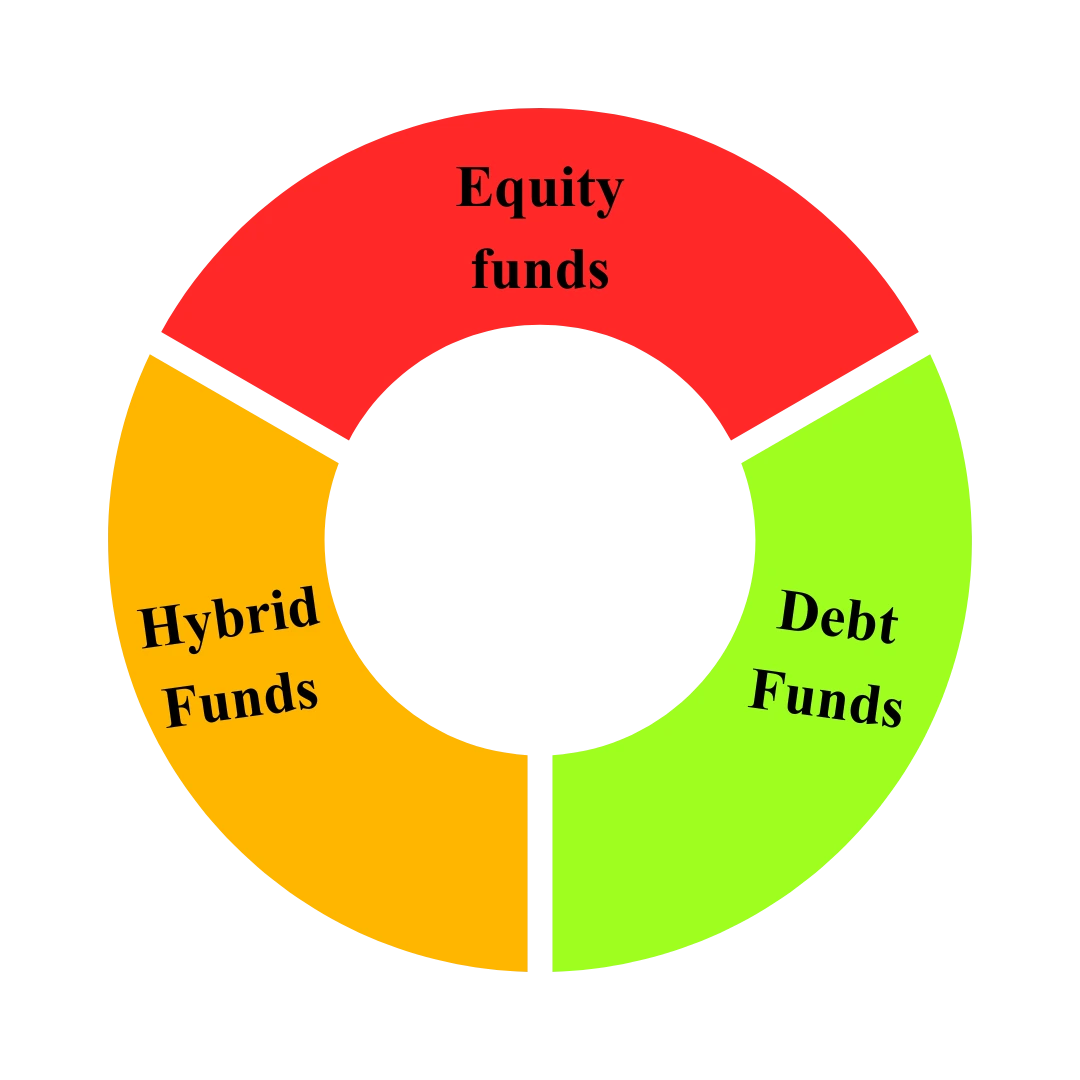
Category Of Mutual Fund
Type of Mutual Fund
Why To Invest In Mutual Funds?
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Professional Management | Experts make investment decisions on your behalf. |
| Diversification | Money is spread across different assets, reducing risk. |
| Affordable Investment | You can start with a small amount through SIP or lump sum. |
| Easy to Buy & Withdraw | Most mutual funds offer high liquidity whenever you need money. |
| Safe & Regulated | In India, mutual funds are regulated by SEBI to protect investors. |
Types of Mutual Funds
| Type | Invests In | Suitable For |
|---|---|---|
| Equity Funds | Shares of companies | Long-term growth, higher risk |
| Debt Funds | Bonds and fixed-income securities | Stability and lower risk |
| Hybrid Funds | Combination of equity and debt | Balanced growth and safety |
| Index Funds/ETFs | Replicate market indices like Nifty 50 or Sensex | Low-cost, passive investing |
The Power of Compounding
The power of compounding is one of the most effective ways to grow wealth over time. It works on a simple principle — the returns you earn on your investment start generating their own returns. Instead of earning profit only on your initial amount, you earn profit on both the principal and the accumulated returns. This creates a snowball effect, where your money grows faster the longer you stay invested. Compounding works best when you start early, invest regularly, and stay patient. Even small investments can become significant amounts over time due to this exponential growth. It is widely used in mutual funds, fixed deposits, retirement planning, and SIPs. The key to benefiting from compounding is time and consistency. In short, compounding turns time into your greatest financial ally, helping you build long-term wealth effortlessly.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Mutual Funds
A mutual fund is an investment option where money from many people is pooled together and invested in stocks, bonds, or other assets by professional fund managers.
Returns are earned from the increase in the value of the invested assets and from dividends or interest. These returns are shared among investors based on their investment amount.
SIP allows you to invest a fixed amount regularly (monthly/weekly) in a mutual fund instead of investing a large amount at once.
All investments carry some risk, but mutual funds are regulated by SEBI (in India) and offer diversification, which helps reduce risk.
NAV (Net Asset Value) is the price of one unit of a mutual fund. It is calculated by dividing the total value of the fund’s assets by the total number of units.
Yes, most mutual funds (especially open-ended funds) allow you to withdraw your money anytime. Some funds may have exit loads if withdrawn early.
You can start investing in mutual funds with as low as ₹500 through SIP, depending on the fund.
No, returns are not guaranteed. They depend on market performance, but diversification and expert management help reduce risk.
Mutual funds are managed by experienced and qualified fund managers on behalf of the investors.
Mutual funds are a smart choice because they offer diversification, professional management, low entry amounts, liquidity, and long-term wealth growth.

